Spiral wound tube heat exchanger
Spiral wound tube heat exchangers are the general term for shell and tube heat exchangers in which one or more streams of tub-side media flow inside spiral wound heat exchange tubes and conduct interwall heat exchange with shell-side media through the heat exchange tubes. They have a compact structure, small temperature difference stress, can contract by themselves, have a large heat transfer area per unit volume, and can achieve multi-stream and multi-phase flow heat exchange processes. They have the advantages of high efficiency, intensification and energy conservation. Since the 1980s, with the development of large-scale complete set of equipment projects in fields such as natural gas and coal chemical industry, spiral wound tube heat exchangers have begun to be widely applied in areas such as natural gas liquefaction, low-temperature methanol washing, low-temperature liquid nitrogen washing, and air separation, becoming indispensable heat exchange equipment for such processes.

Figure 1 shows the core of a large wound tube heat exchanger
Structural type
The spiral wound tube heat exchanger mainly consists of main structures such as heat exchange tubes, central cylinders, positioning elements, wrapped cylinders and shells. The core component is the spiral heat exchange tube, which is usually made of stainless steel or other corrosion-resistant materials and can be tens or even hundreds of meters in length. According to the working conditions, welded pipes and seamless pipes are mainly used. The heat exchange tubes are spirally wound around the central cylinder in a single or multi-tube welding manner. The winding directions of adjacent layers are opposite, and the winding Angle is generally between 3° and 20°. The spacing of the tubes is adjusted by flat spacers and special-shaped spacers to ensure the radial and axial spacings between the heat exchange tubes, and they are fixed with pipe clamps. The heat exchange tubes and the tube sheet generally adopt a connection structure of strength welding and expansion. Their two ends are welded or connected to the tube sheet to form a closed fluid channel. The central cylinder has certain strength and rigidity and plays a supporting role in the core body. | 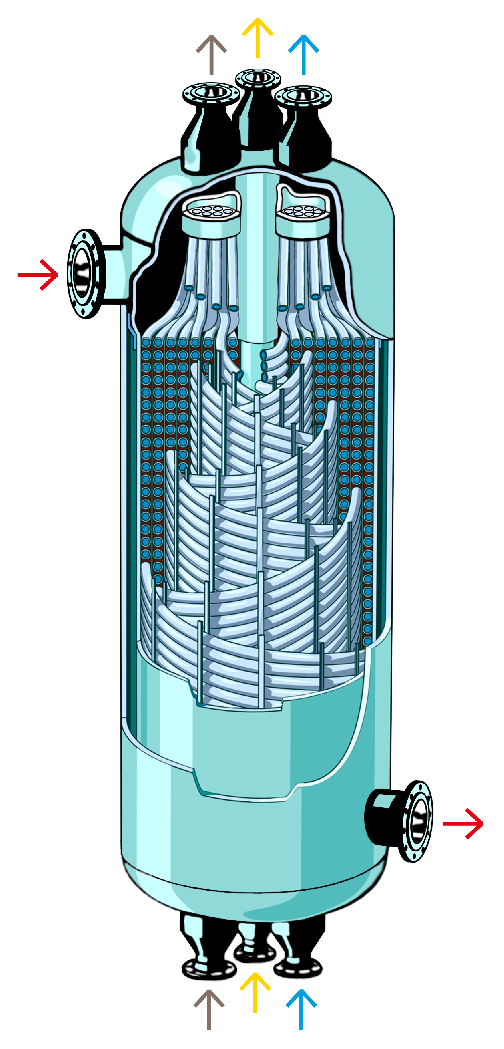 |
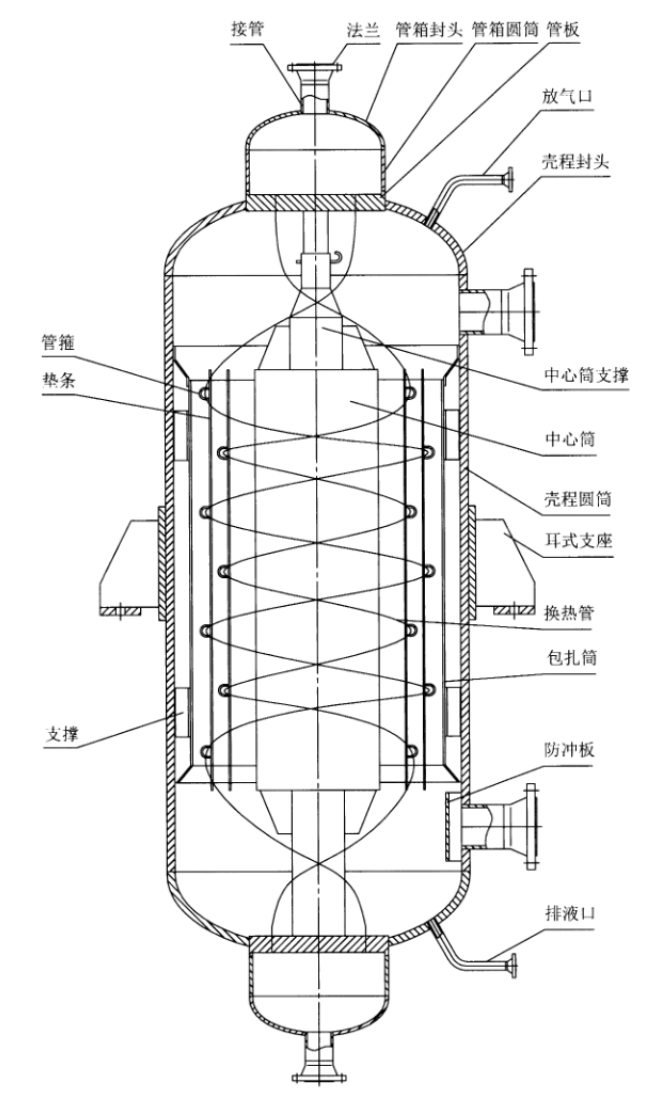 | 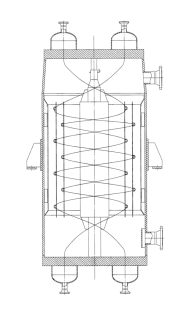 | 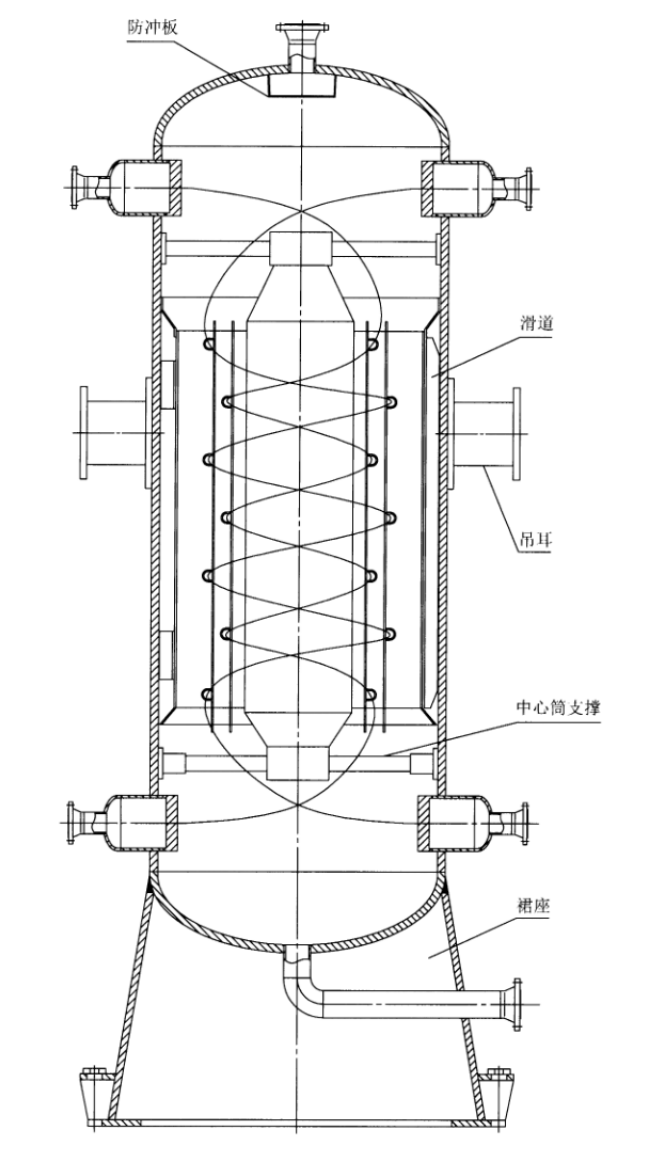 |
| Figure 3 shows a single-stream integral tube sheet heat exchanger wound around tubes | Figure 4 shows a multi-stream integral tube sheet heat exchanger with zoned tube layout | Figure 5 Split tube sheet heat exchanger |
Advantages and features
Due to the thinness and high strength of the heat transfer tubes on the tube side, the wound tube heat exchanger can withstand a maximum operating pressure of 20MPa, and thus can be used in high-pressure working conditions. The spiral wound tube heat exchanger is composed of two or more spiral channels. When the fluid flows in the spiral tubes, a secondary circulation is formed, which enhances the heat exchange effect and helps to reduce the deposition of dirt. This gives the heat exchanger a certain self-cleaning ability. The fluid flows approximately counter-current in both the tube side and the shell side respectively, and the required heat transfer temperature difference to achieve the desired heat exchange volume is relatively small. Both ends of the tube bundle in the wound tube heat exchanger have certain free sections, which can contract or expand by themselves during startup or shutdown to adapt to huge temperature changes. Meanwhile, the wound tube heat exchanger is relatively compact in structure and has a certain self-compensation capacity for temperature. It has better adaptability and reliability, and thus is widely used in various heat exchange equipment.
Application prospects
The application of spiral wound tube heat exchangers is highly competitive in the market for simplifying the process flow and creating a safer and more efficient heat storage and exchange operation environment for equipment. With the continuous advancement of industrial technology and the increasing demand for energy efficiency, the design and application of this type of heat exchanger will be further developed and promoted. Whether in the traditional low-temperature field or emerging fields such as energy storage, spiral wound tube heat exchangers will provide innovative solutions for achieving efficient, reliable and economical heat energy transfer.
The above article is from the Nanjing Future Energy System Research Institute, authored by the Energy Storage Technology Center


Hi there! 🤝 Let’s help you find the right contact at Chenkai. I’ll ask a few quick questions and pass your answers along to the right expert.
Let’s connect you with the right expert! What’s your request about? Just pick one option below 👇